Two of the largest blockchains for DeFi and NFTs are Ethereum and Solana. Both networks have wide ecosystems and individual traits that make them appealing. But how exactly do you compare Solana vs. Ethereum? Solana has been deemed the “Ethereum killer” within crypto communities. But is that really true? Is Solana better than Ethereum?
This article will discuss the main differences between the two blockchains. We’ll be looking at the underlying technology and the core features of each blockchain, as well as the expanding DApp ecosystem.
Want to get the hottest news on ETH and SOL? Join BeInCrypto Trading Community on Telegram: discuss, get ETH & SOL technical analysis and read all the hottest news on coins.
What is Ethereum?
Buy ETH on one of our most loved exchanges:
Ethereum is the first programmable blockchain, which enables developers to build decentralized applications using its general-purpose smart contracts feature.
The Ethereum blockchain can also be used for non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and decentralized finance (DeFi) apps. Ethereum was built with the intention of being everything to everyone and serving a broad range of specialized applications. And that is precisely what it does. It offers security and a complete set of tools to build any decentralized application.
The blockchain’s native asset is ether (ETH), and it is also used for paying the gas fees for transactions. However, Ethereum is currently undergoing a proof-of-stake (PoS) transition, which will bring several benefits to the network, including lower costs.
What is Solana?
Buy SOL on one of our top platforms:

Solana was created to solve the scaling challenges faced by the Ethereum blockchain. This is due to the increasing interest in crypto and the bandwidth limitations that limit transaction throughput for anyone who wants to use a particular blockchain. Solana uses clever technical tricks to find convincing solutions to problems that are not being solved by other blockchain platforms.
Like Ethereum, Solana provides a platform for non-fungible tokens and decentralized applications (DApps). These digital versions of collectors’ items like artworks have created a lot of excitement among digital artists like 3D modelers and visual effects artists.
One of Solana’s first ventures in this direction was Degenerate Apes. This collection contains more than 10,000 portraits that can only be bought in SOL. This can have a significant impact on the currency’s value — the trading volume for Degenerate Apes amounts to tens of millions.
Solana vs. Ethereum: What are the differences?
Both blockchains have their fans and tons of apps already running on them. However, Ethereum is the most popular because it offers a more transparent and sophisticated ecosystem of DApps. Certain differences can’t be overlooked between the two. We will examine the differences between these blockchains from ten different perspectives.
1. Mechanism
Ethereum 1.0 relies on a PoW consensus mechanism, which is the same mechanism used by Bitcoin’s blockchain. This means that the network is protected by miners, who use their computational power to validate blockchain transactions and generate new blocks. This is the essence of the decentralized network, and it serves to increase the security of the network.
However, the PoW mechanism can only process a few transactions per second, which is a huge impediment to a growing decentralized network. Therefore, in September 2022, Ethereum switched to proof-of-stake. This upgrade, Ethereum 2.0, was achieved by merging with Beacon Chain, a blockchain operating on PoS.
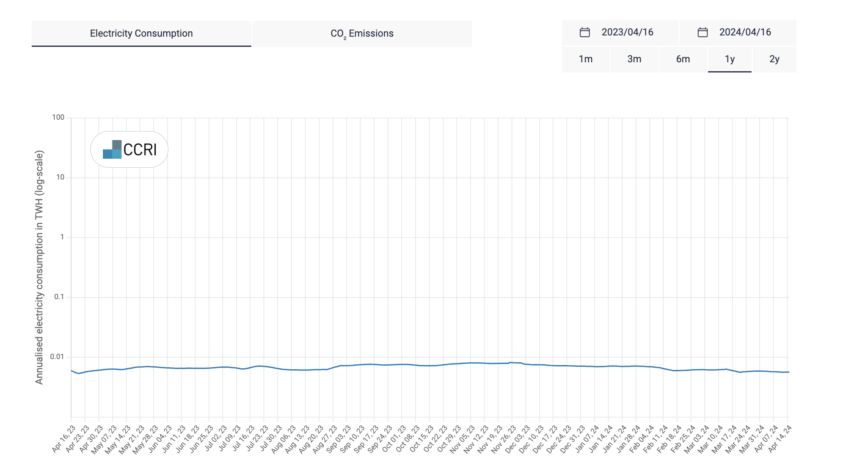
The decision to move to PoS was also fueled by Ethereum’s commitment to sustainability and reducing its carbon footprint. This objective was successfully achieved, at least when we look at Ethereum’s annualized energy consumption. According to the Crypto Carbon Ratings Institute (CCRI), from April 2023 to April 2024, Ethereum maintained a steady electricity consumption rate.
Despite the expectations that the shift from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake would significantly reduce energy use, the data, captured on a logarithmic scale, suggests no substantial change occurred during this period. This steady state implies that any impact of the transition to a more energy-efficient consensus mechanism had already taken effect.
Solana is different from Ethereum in that it uses proof-of-history (POH). In essence, it requires a series of computational steps to determine the cryptographical time between two events. You can track each transaction’s order by adding timestamps and adding them to transactions. This order sequencing fundamentally differs from the one in Bitcoin or Ethereum, where transactions are not placed promptly.
Another essential difference between Ethereum and Solana is its “stateless” architecture. This helps to reduce memory consumption. Because the entire network’s state does not need to be updated for every transaction, transactions can be performed sequentially. This makes Solana extremely scalable.
2. Solana vs. Ethereum: Programming language

Developers can create programs using smart contracts that run on decentralized blockchain networks. Each node on the network hosts its own virtual machine that executes instructions as they are added to the digital ledger.
The security of smart contracts is affected by the programming languages that a smart contract platform supports and the virtual machines it uses.
Of course, the programming language used is important as developers who are more familiar with it will be less likely to make mistakes. This means that an older virtual machine might be more stable and have fewer errors than one that is newer.
Ethereum uses the custom-built Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Its smart contracts are written primarily in custom languages such as:
- Solidity (inspired by C++)
- Viper (Pythonic Language)
- Yul/Yul+ (intermediate language to EVM)
- Fe (based on Rust and Python)
Conversely, Solana prefers to use more well-known languages like C, C++, and Rust.
Solana’s architecture is more complicated and supports multithreading. It also uses the Gulf Stream transaction forwarding mechanism to run its programs instead of mempools.
The details of Solidity, the programming language used by Ethereum, can create many vulnerabilities in Ethereum smart contracts when used by inexperienced developers. Although Solana uses more familiar programming languages, the complex architecture can pose security risks when experienced programmers don’t thoroughly audit code.
3. Decentralization

Decentralization stands at the core of blockchain technology. And it is one of the main differentiators when comparing Solana with Ethereum. The ultimate goal is to eliminate systems in which an individual or group has significant control over them. This helps to prevent abuse of power and improves resilience.
However, decentralization can also pose a challenge in blockchain systems. PoW networks led the way to mining pools, which created an environment where several groups could have centralized control over the blockchain.
PoS, on the other hand, is a system where the highest stakeholders receive the greatest rewards. This “rich get richer” design can allow for the centralization of power.
Solana is more centralized than Ethereum. Solana’s top 30 validators hold over 35% of the total stake. The top validators have thousands of SOL staked and control a significant percentage of the network.
4. Downtimes
Ethereum is the first programmable blockchain network and most of its flaws have been sorted out since its inception. Although it can sometimes get congested, it is never down because it is significantly more decentralized than other chains. It’s actually part of the reason Ethereum has struggled to scale. The project wants every crypto user to be capable of running an Ethereum node on any hardware. Since its inception, Ethereum has never been down.
Solana is, however, still struggling with some of the challenges of creating a truly decentralized network. The chain has experienced several downtimes since its inception.
The first Solana outage took place in Dec. 2020. It lasted for five hours, and no funds were lost. The second Solana outage took place in Sep. 2021. It lasted for 17 hours. This downtime was caused by a DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack.
A DDoS attack is when a malicious actor attempts to overwhelm a network. What was the result? Solana was halted for several hours and lost some of its investors, but no funds were lost.
However, the network experienced a third shutdown, which was not the result of an attack. In Jan. 2022, bot swarms overloaded the network during an Initial DEX Offering. According to reports, the network reached a peak of 400,000 TPS (transactions per second). While this downtime is alarming, the fact that Solana could handle up to 400,000 TPS is impressive.
Decentralization helps reduce the possibility and impact of downtime. Furthermore, increasing a network’s size by adding nodes makes it more decentralized and contributes to its byzantine fault tolerance (BFT). BFT is a distributed system’s ability to identify and reject false information. When you put together decentralization and strong BFT, you get an extremely robust blockchain.
5. Transaction cost
This is crucial as many people hate to pay transaction fees. Solana is well-known for its low transaction fees. Ethereum has a higher transaction cost than Solana.
As of April 2024, the average gas fee on the Ethereum network is 18.45. Solana’s gas fees stand at an average of 0.0001 SOL per transaction. The Solana blockchain has a block time of 0.4 seconds and a block size of 20,000 transactions, compared to Ethereum’s block time of 13 seconds and block size of only 70 transactions.
Block size is handled differently between blockchains. Some block sizes are determined in terms of storage (i.e., MB in Bitcoin), while others are determined by gas limit (i.e., gwei in Ethereum). Therefore, in the latter (gas limit), transactions per block will be variable. Ethereum’s block size has a gas limit of 30 million. An optimal blockchain will want to include as many transactions as possible while limiting gas usage.
6. Transaction speed
Solana is actually one of the fastest blockchains when it comes to processing transactions. This is due to the network architecture. Ethereum prioritized decentralization, while Solana was more focused on throughput.
Ethereum 1.0 can theoretically handle up to 30 TPS, but realistically caps out between 12-15 TPS. ETH 2.0 processes about 20-30 TPS. This number will likely increase once shards are introduced. Ethereum 2.0 revolutionizes the ETH network with its upgrade, increasing the potential throughput to up to 100,000 transactions per second (TPS), reducing transaction fees, and strengthening network security.
These enhancements will likely drive faster adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) due to the higher TPS and reduced costs. On the other hand, Solana can process more than 50,000 TPS. Visa, the worldwide payment processor, can handle 65,000 TPS.
7. Network size
Ethereum is the largest network that supports smart contracts. According to DeFi Llama as of April 16, 2024, Ethereum’s TVL (Total Value Locked) is up to $49.03 billion, while Solana’s TVL is at $3.451 billion. This means that most financial apps prefer Ethereum.
8. Market cap
Both Ethereum and Solana have their own native coins that are used for paying the transaction fees. These are some of the two most important coins in the entire crypto market.
As of April 16, 2024, 1 ETH is $3,208.74 and the market cap of Ethereum stands at $372 billion. Ether ranks as the second cryptocurrency, just under Bitcoin.
The Solana network also doesn’t have a fixed maximum supply of SOL. However, it does have a fixed inflation rate, which is diminishing over time, as it tends to reach 1.5% in the long run. As of April 16, 2024, 1 SOL equals $130.56 with 378.25 million SOL in circulation. This makes the market cap of Solana is around $61 billion.
9. DeFi ecosystem
Given the age of Ethereum, it has a much larger and more diverse DeFi ecosystem than Solana. However, Solana is trying hard to attract more developers to the network by launching a variety of marketing strategies such as hackathons and bug-bounty programs. Since its inception, these tactics have helped to increase the number of users and developers.
Ethereum is the main network for some of the most used DeFi apps, such as MakerDAO, Lido, Uniswap, and Aave. Moreover, 2021 brought a new trend to the blockchain world, which is the NFT craze. The most popular NFT marketplaces are built on Ethereum.
It’s important to point out that the DeFi ecosystem on Solana remains in its infancy. However, there are several Solana DApps that are starting to attract new users. This is due to extensive hackathons. Some of the most DeFi apps on Solana are Solend and Raydium.
Since blockchain is still a new technology, the ecosystem is still developing. There is a strange correlation between Solana and Ethereum – whenever Ethereum’s gas fees rise, Solana users seem to increase.
While nobody can predict the future, we can say that the current DeFi ecosystem of Ethereum is more extensive and offers a broader range of applications.
10. NFTs

Although Ethereum wasn’t the first to use non-fungible tokens to create NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), it was one of the most important protocols to promote them. Although the trading of NFTs exploded in 2021, NFTs have been used far long before that.
CryptoKitties was one of the first blockchain apps to have NFTs. It became media-worthy when the app caused a huge congestion on Ethereum in 2017.
Solana allows buyers to buy NFTs with no transaction fees and few congestion issues. It means that Solana and SOL NFTs can be more easily accessed than those on Ethereum.
The price of Solana’s NFTs started picking up in the second half of 2021. In Sep. 2021, a Degenerate Ape NFT was sold for $1.1 million. This sale marked the first million-dollar NFT transaction on the Solana network. A Solana Monkey sold for $2 million in Oct. 2021.
Solana vs. Ethereum: Which one is better?
When comparing Solana vs. Ethereum, it’s important to pinpoint the exact features or needs for your actions on the blockchain. If you’re a developer, you will be very interested in the underlying technology, which is the main topic when comparing Ethereum with Solana. Furthermore, each blockchain has its own consensus mechanism and has different ways of scaling. Solana is the fastest blockchain, but Ethereum has a much higher trading volume and is more used in the crypto market.
Investors may be more interested in the growth prospects of the two networks. As the decentralized world expands, one may assume that both of these networks will grow in the future. But how much will the growth be, and what will be the fate of their coins? This is something that is worth looking into.
*This ad promotes virtual cryptocurrency investing within the EU (by eToro Europe Ltd. and eToro UK Ltd.) & USA (by eToro USA LLC); which is highly volatile, unregulated in most EU countries, no EU protections & not supervised by the EU regulatory framework. Investments are subject to market risk, including the loss of principal.
Frequently asked questions:
Both Ethereum and Solana are what’s known as smart contract platforms. In order to build decentralized applications, blockchain protocols will double as virtual machine to host smart contracts. This makes Ethereum and Solana competitors.
A blockchain’s popularity can be split between: those that build on the blockchain, and those that use or transact on the blockchain. In terms of active developers and network activity, Ethereum is more popular than Solana. Ethereum has been around longer and has had more time to grow its network’s value and total value locked (TVL).
Solana’s technology allows for much faster transaction processing. However, this frequently leads to forking, and subsequently the blockchain often needs to reset. Ethereum has more uptime than Solana, and thus better technology
No. Ethereum is more secure than Solana. It has more active members in the community and developers. Solana lacks the security insights that Ethereum has achieved after seven years (2015) since its launch.
The crypto spaces have often referred to Solana as the “Ethereum killer” due to its similar role in the crypto world. They both enable developers to build decentralized apps.
Solana could be just as large as Ethereum, if it manages to attract more developers to launch their apps on the Solana network. As of 2022, there is a huge gap between the two networks, and Ethereum has a TVL (Total Value Locked) that is 95% higher than Solana’s TVL.
Solana boasts a higher transaction speed than Ethereum, thanks to its unique consensus mechanism combining proof-of-history (PoH) with proof-of-stake (PoS). Solana’s network can process up to 65,000 transactions per second (TPS), whereas Ethereum, currently on PoS after the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, handles about 30 TPS. However, Ethereum’s upcoming sharding proposal is expected to increase its capacity, allowing it to process more transactions per second.
Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities are more established, having a larger developer community and more deployed decentralized applications (DApps). It uses a robust programming language called Solidity, which has become a standard in the industry. Solana uses Rust and C for smart contract development, offering high performance and efficiency, which may appeal to developers looking for faster execution times and lower costs. Solana is gaining traction for its smart contract capabilities but is still building a community and ecosystem comparable to Ethereum’s.
Trusted
Disclaimer
In line with the Trust Project guidelines, the educational content on this website is offered in good faith and for general information purposes only. BeInCrypto prioritizes providing high-quality information, taking the time to research and create informative content for readers. While partners may reward the company with commissions for placements in articles, these commissions do not influence the unbiased, honest, and helpful content creation process. Any action taken by the reader based on this information is strictly at their own risk. Please note that our Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and Disclaimers have been updated.




